1y, Epileptic seizures
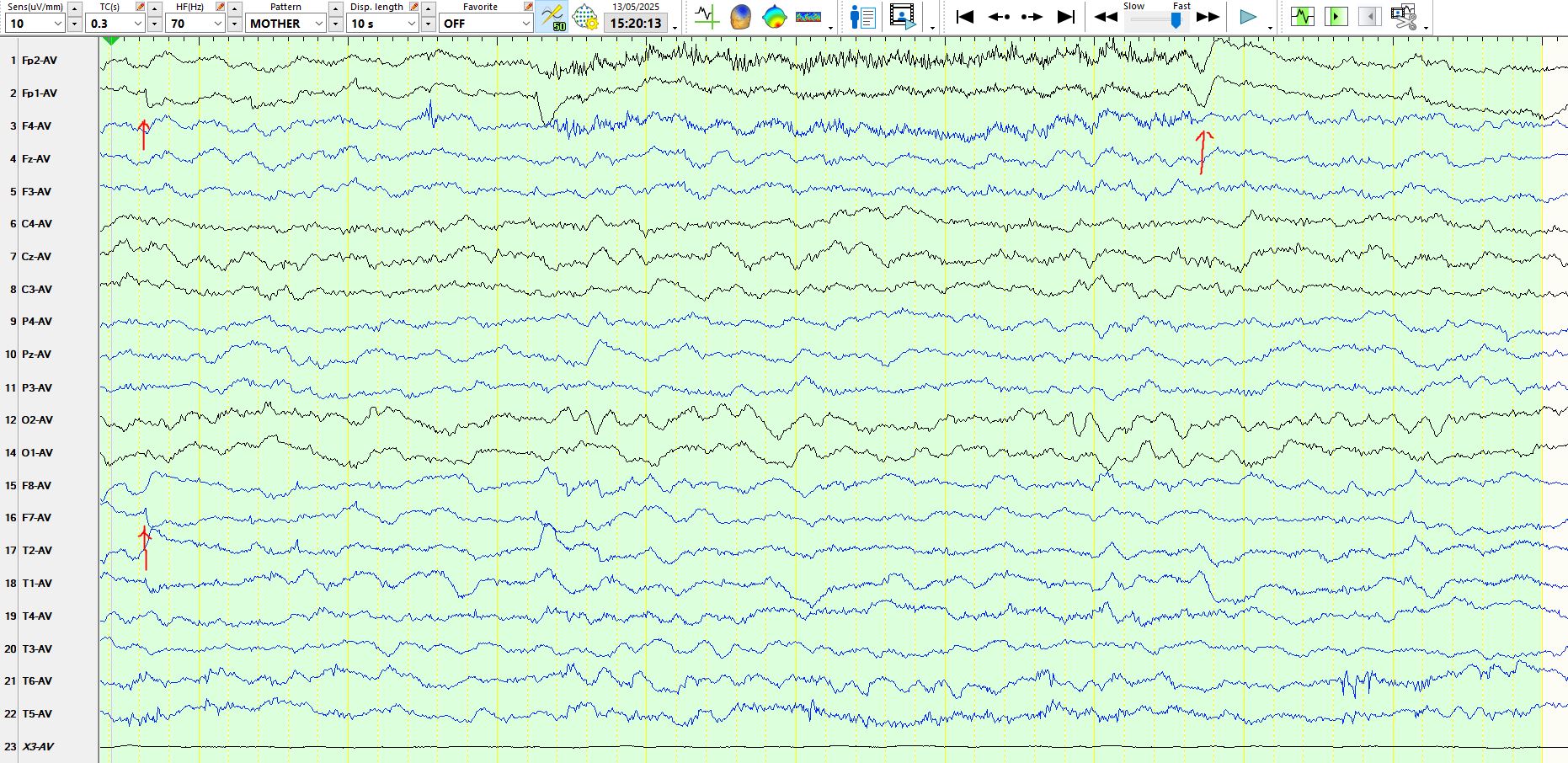
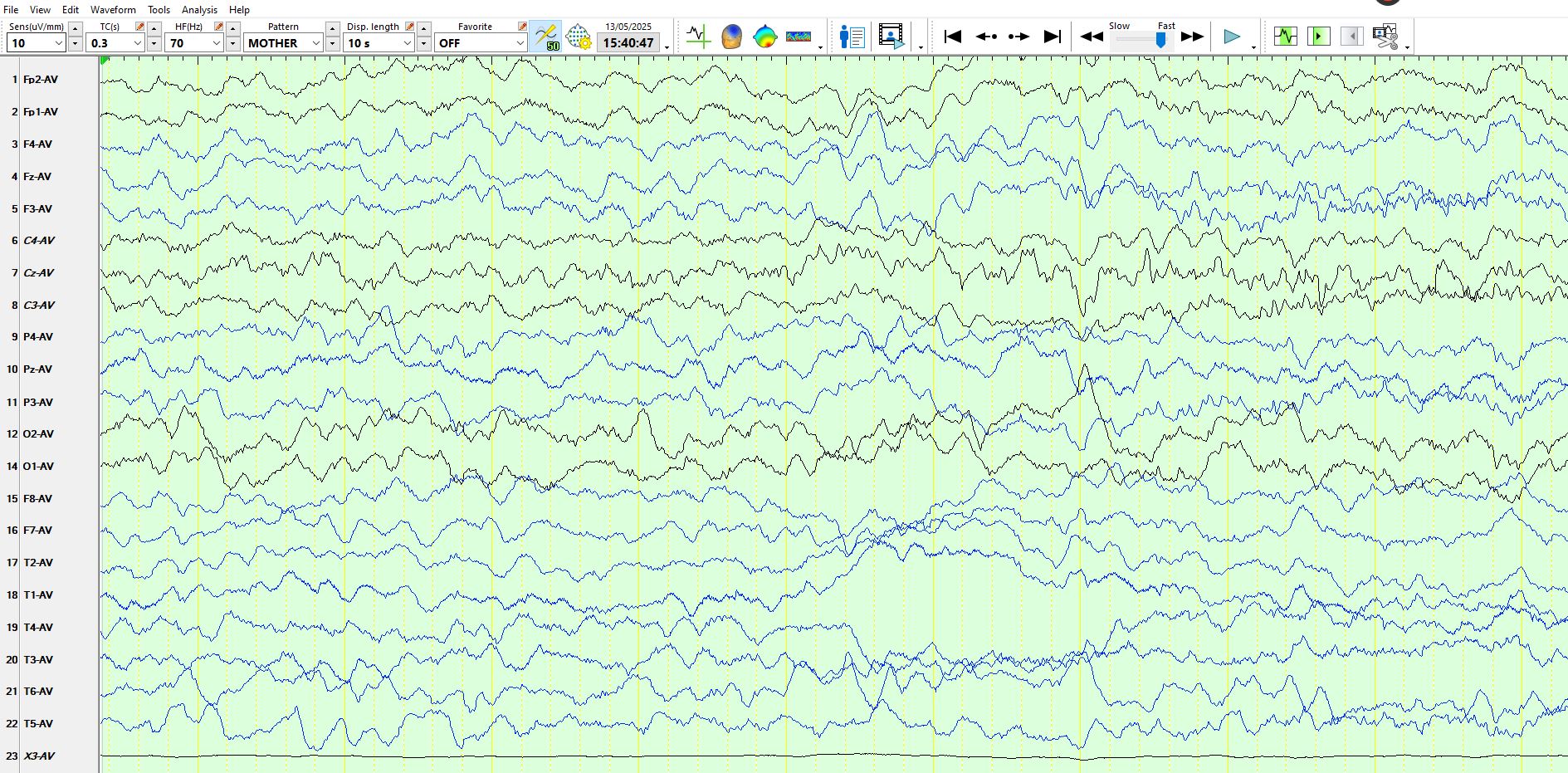
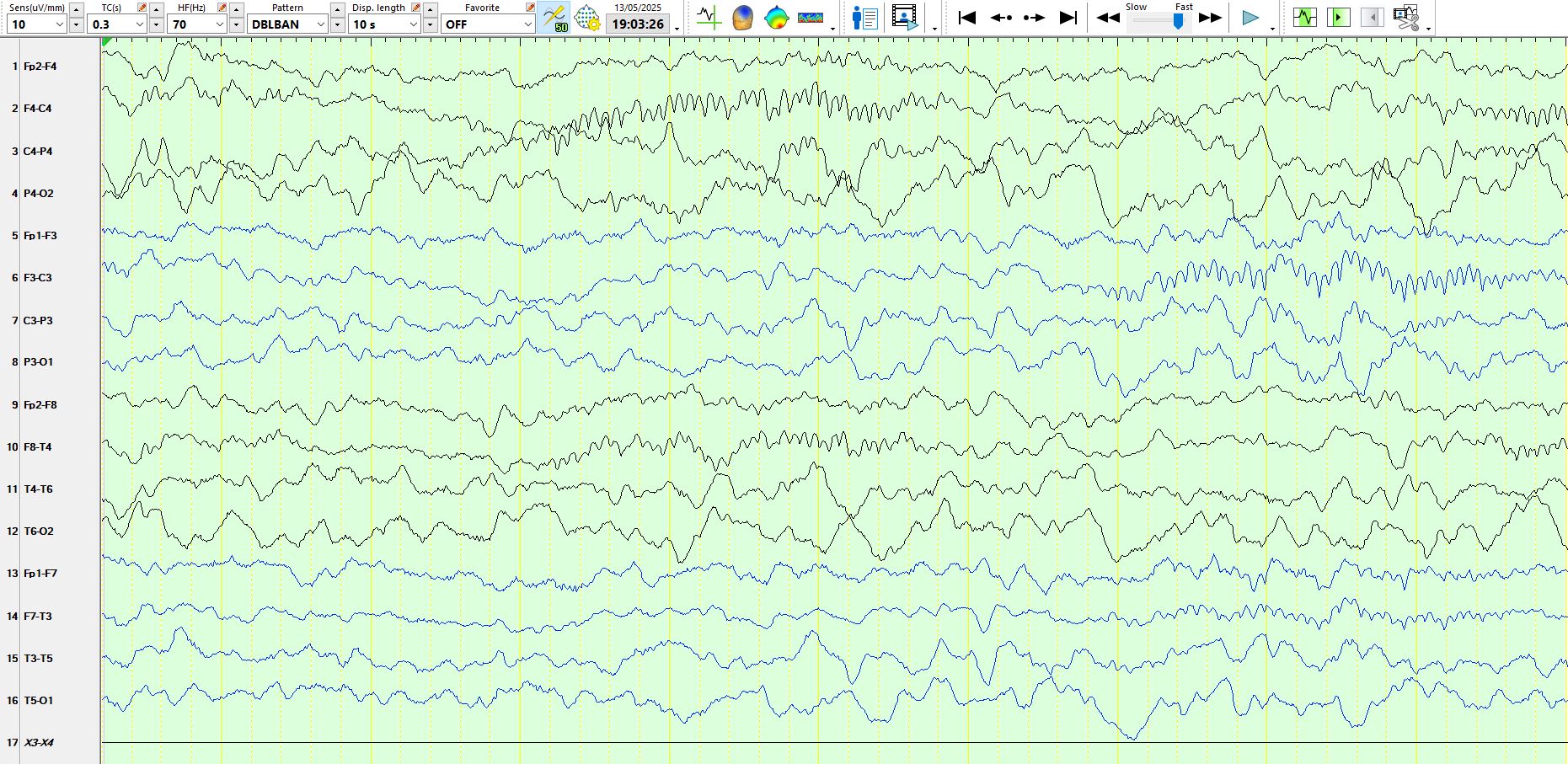
May 14, 2025Above: Awake, normal background rhythms for age (principally theta frequencies over the posterior head regions and beta frequencies that are best developed at CZ), oblique eye movement (first arrow) and an eyeblink (2nd arrow)
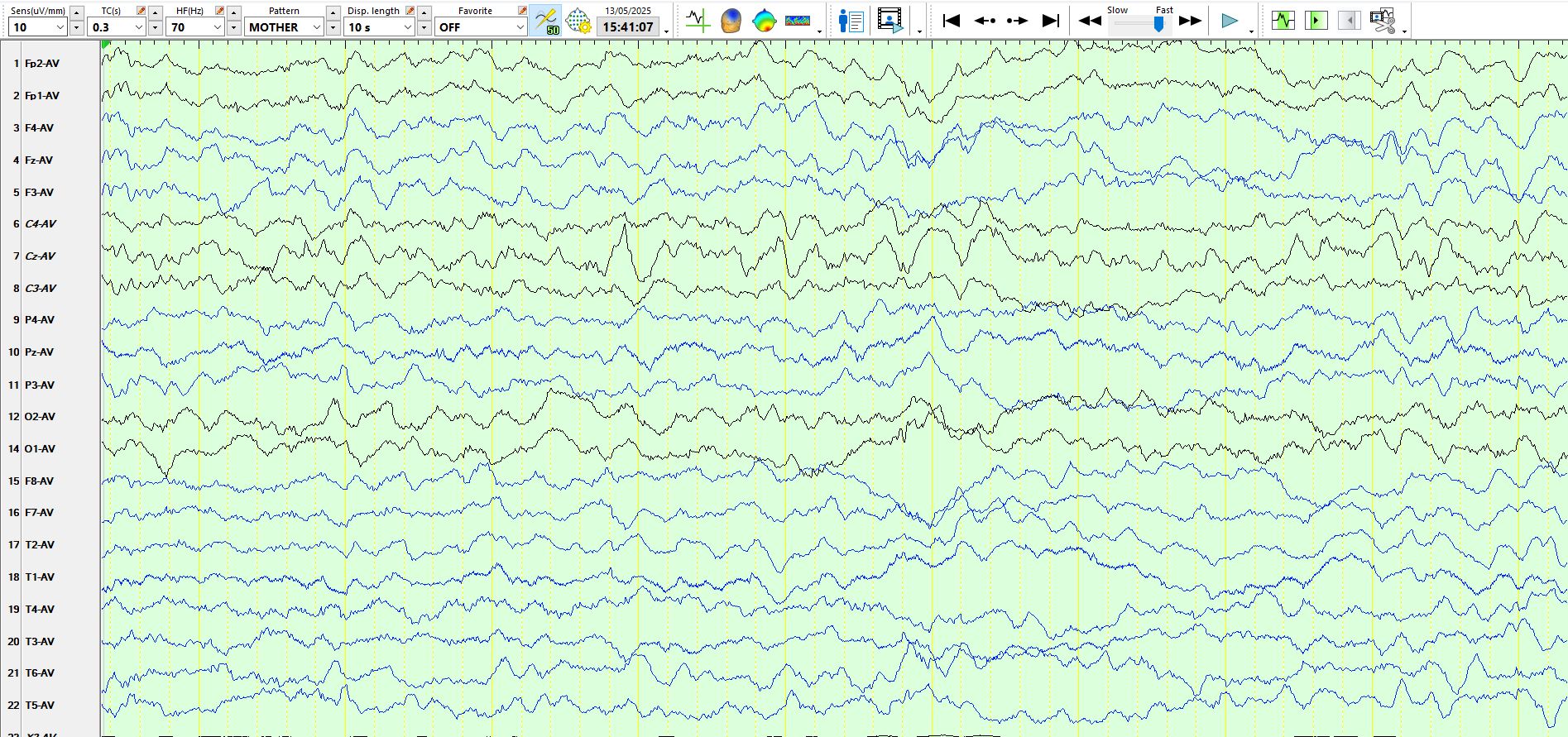
The EEG demonstrated repeated events resembling the above 2 epochs
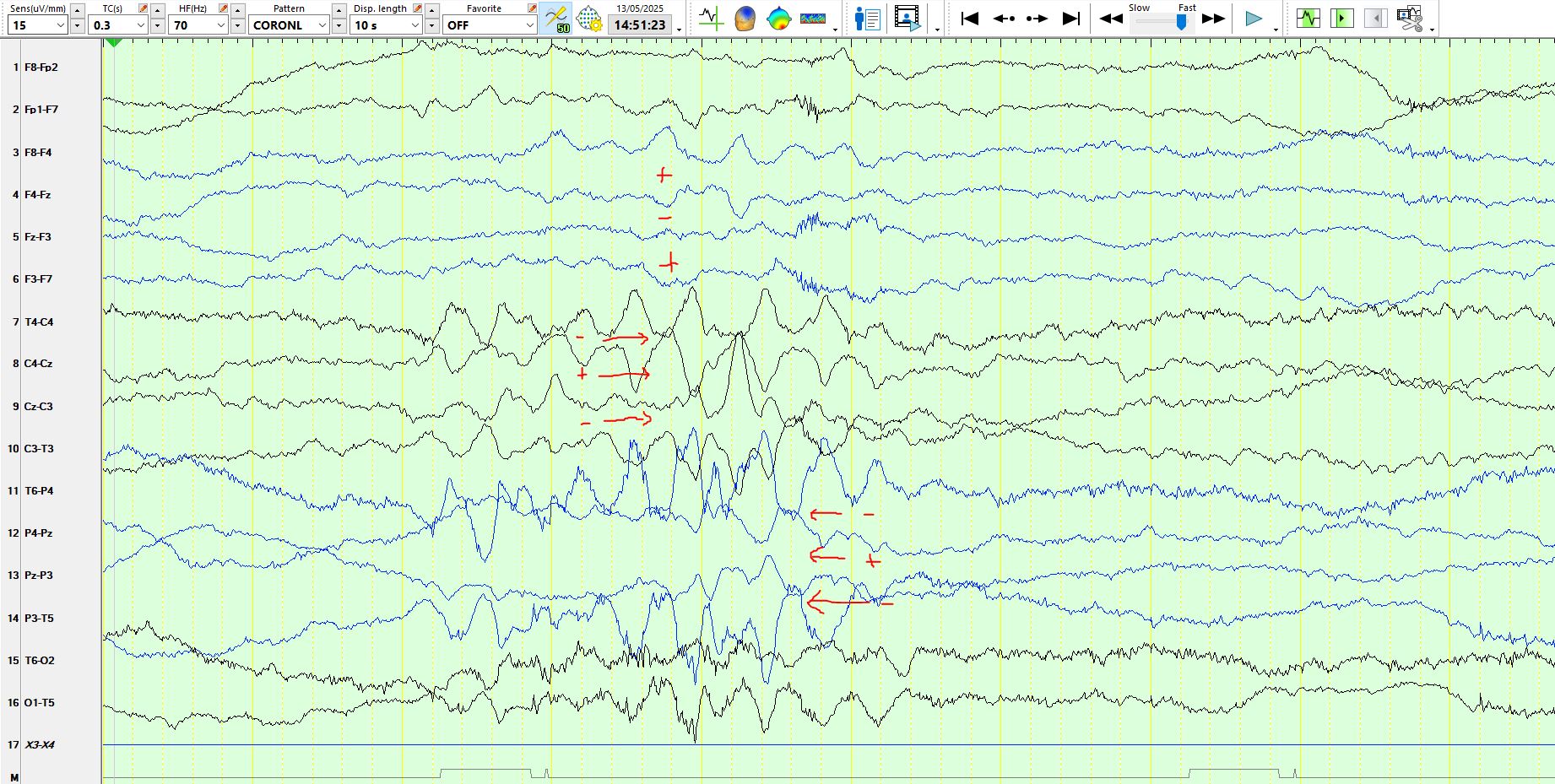
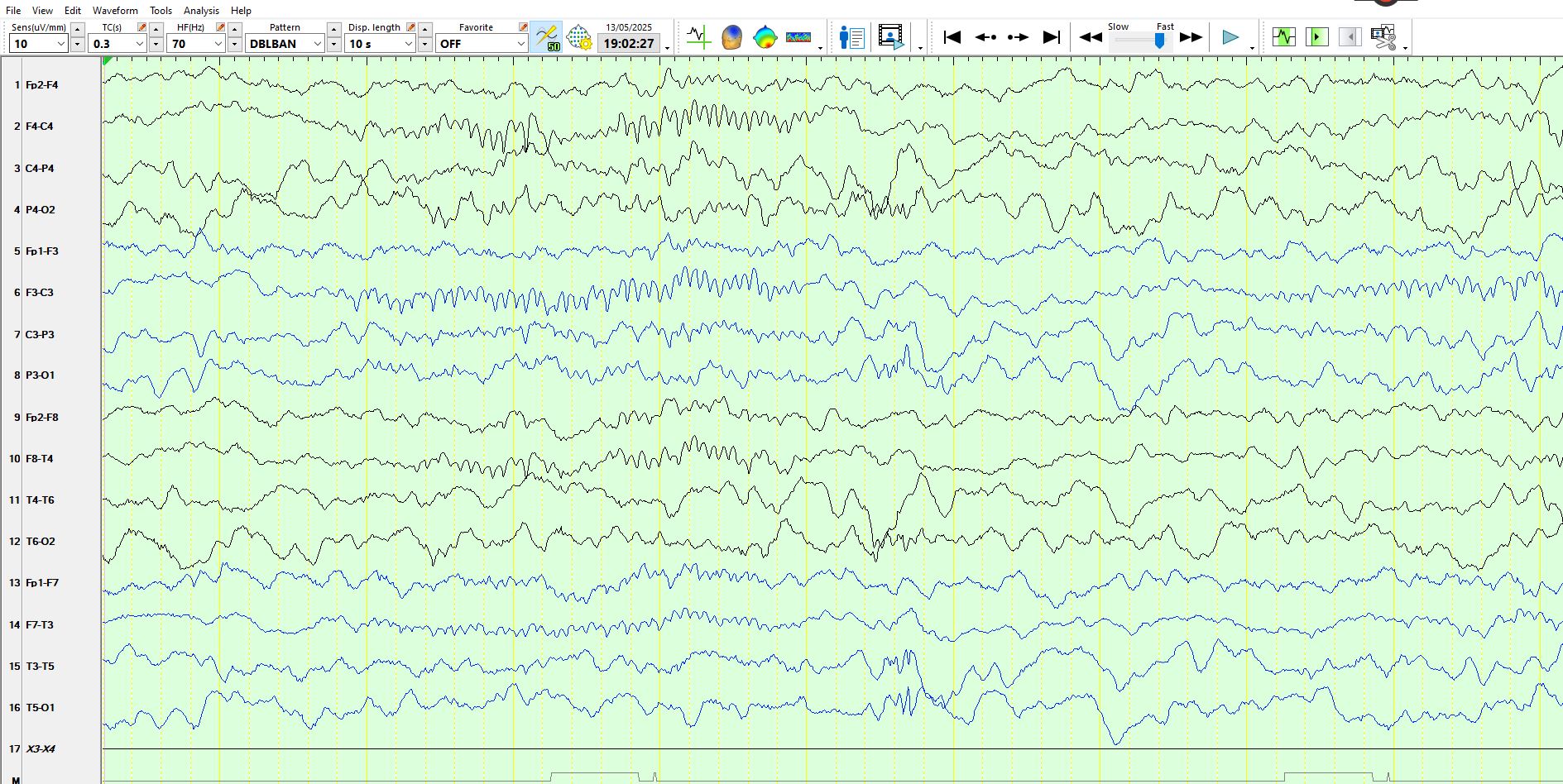
In this instance it is best to change the sensitivity to allow better scrutiny of the waveforms, which reveal the phenomenon of "double cancellation" on the coronal montage. Notice that adjacent derivations in the coronal plane are negative, then positive, then negative, as illustrated above. Hence, these can confidently be called movement artefacts. The video demonstrated that the child flapped his arms up and down while lying on his back on the bed, synchronous with the above waveforms each occasion.
The following are sequential pages, 40s in total:
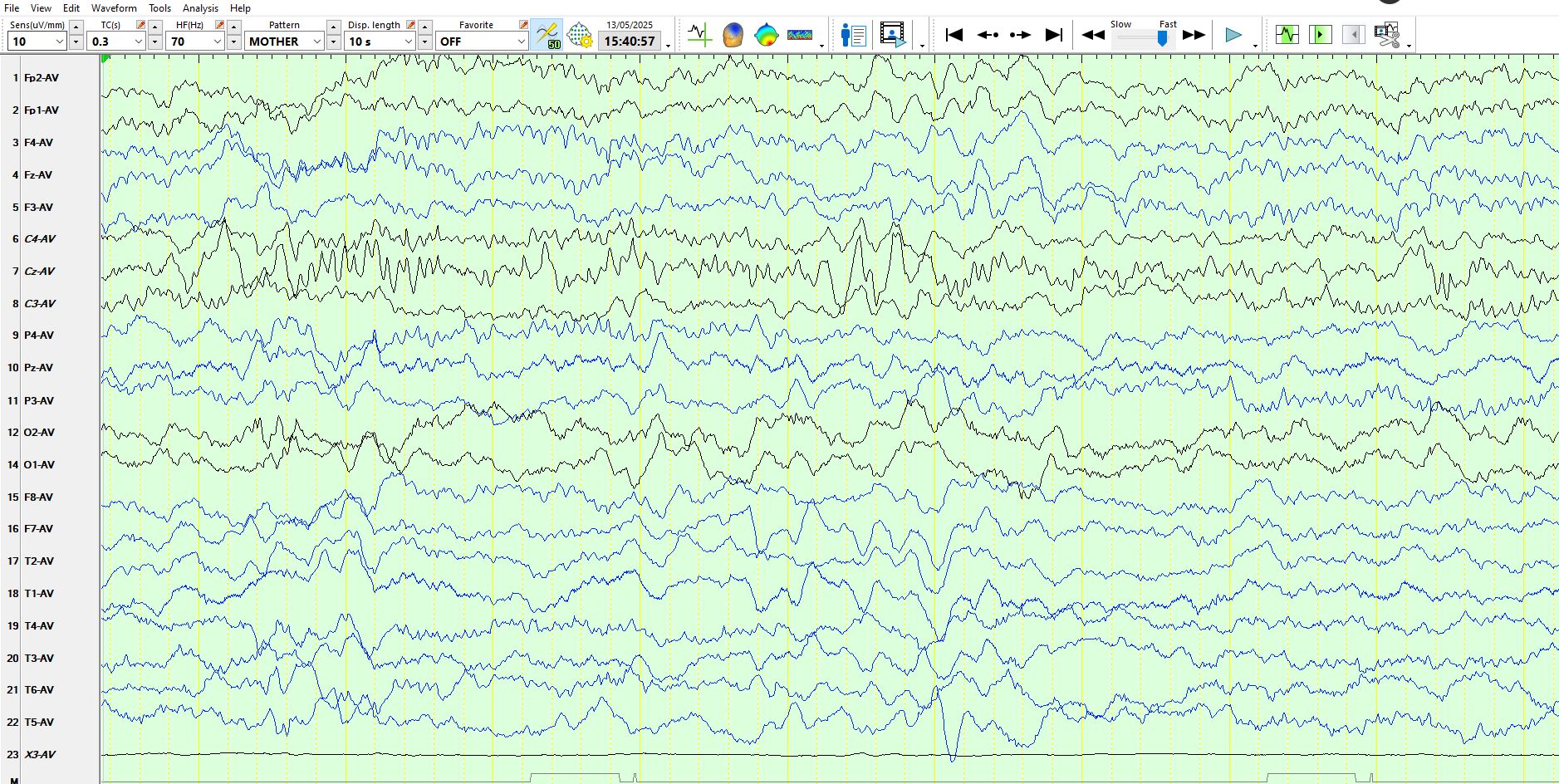
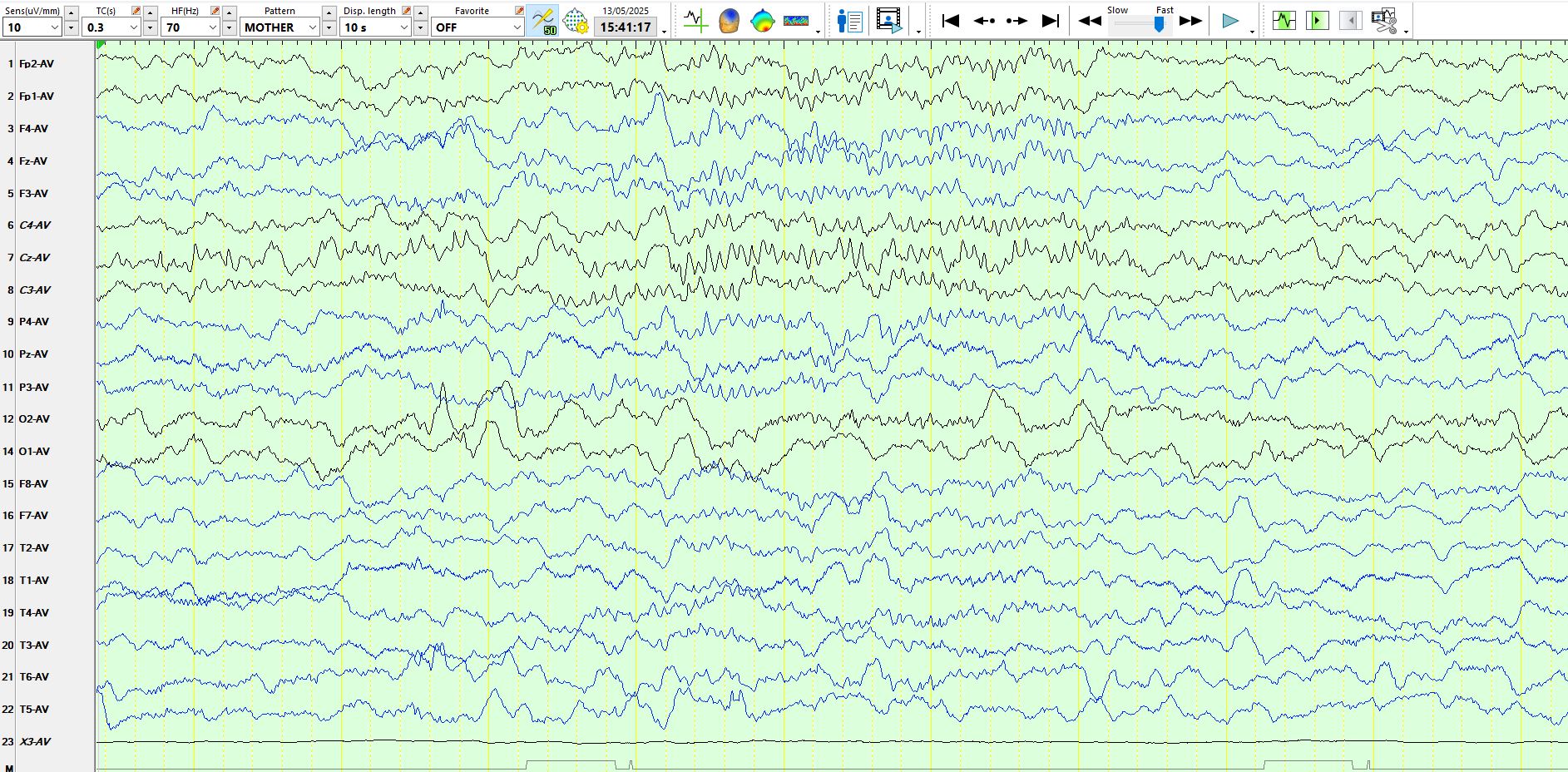
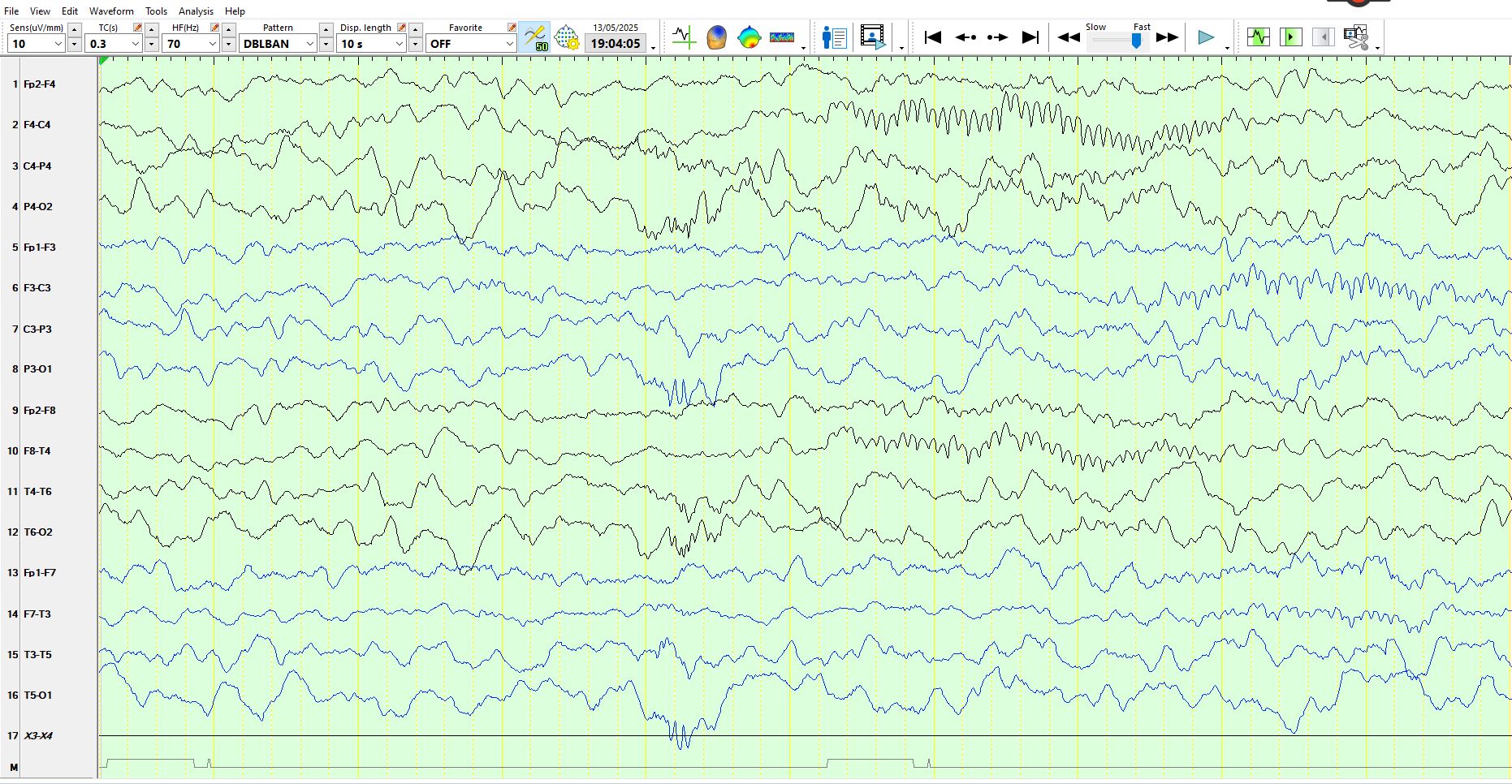
Notice duration of the spindles above and the shifting location of these. These are normal for age.
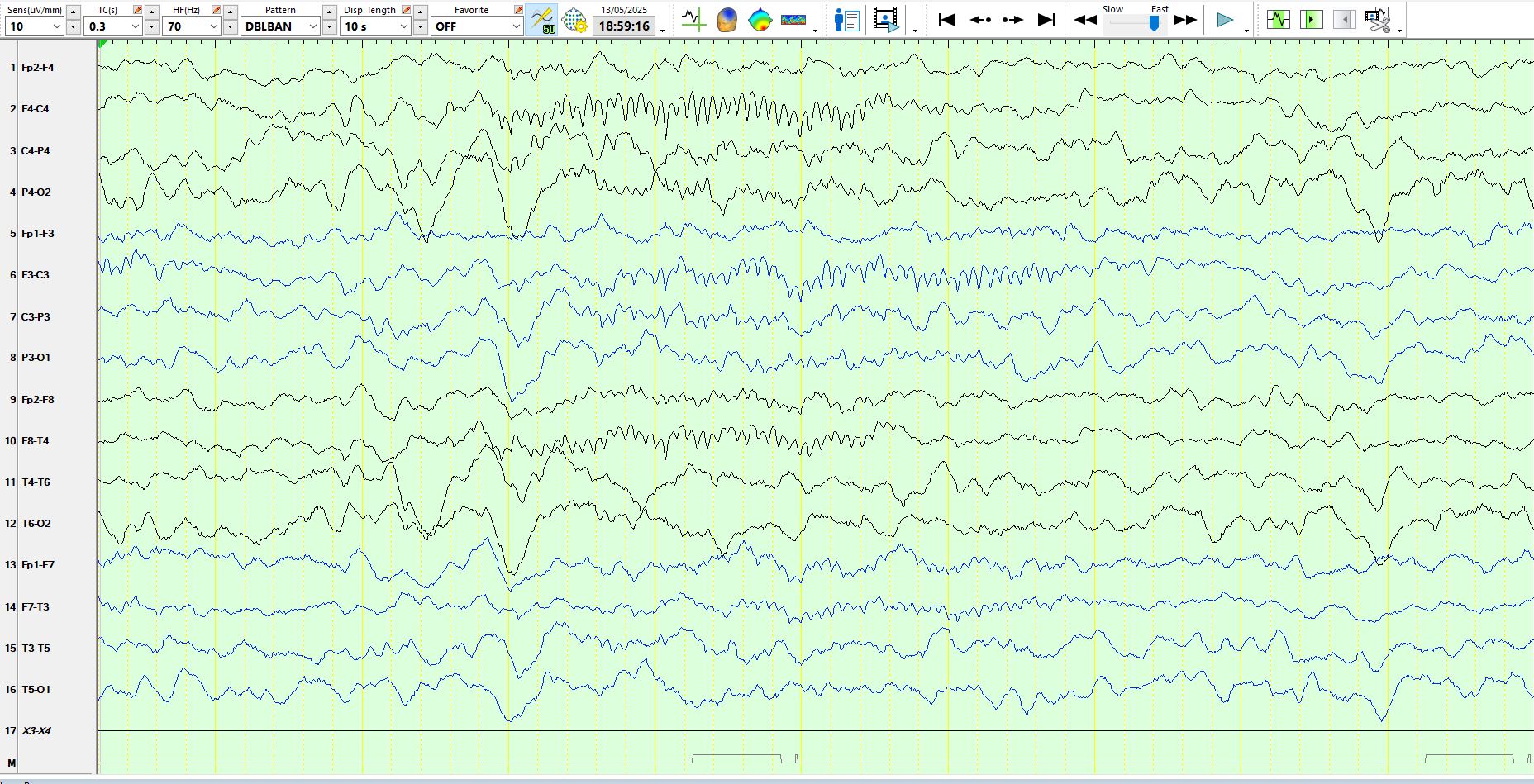
Above: Polyspikes Over the occipital, parietal and posterior temporal regions bilaterally and synchronously
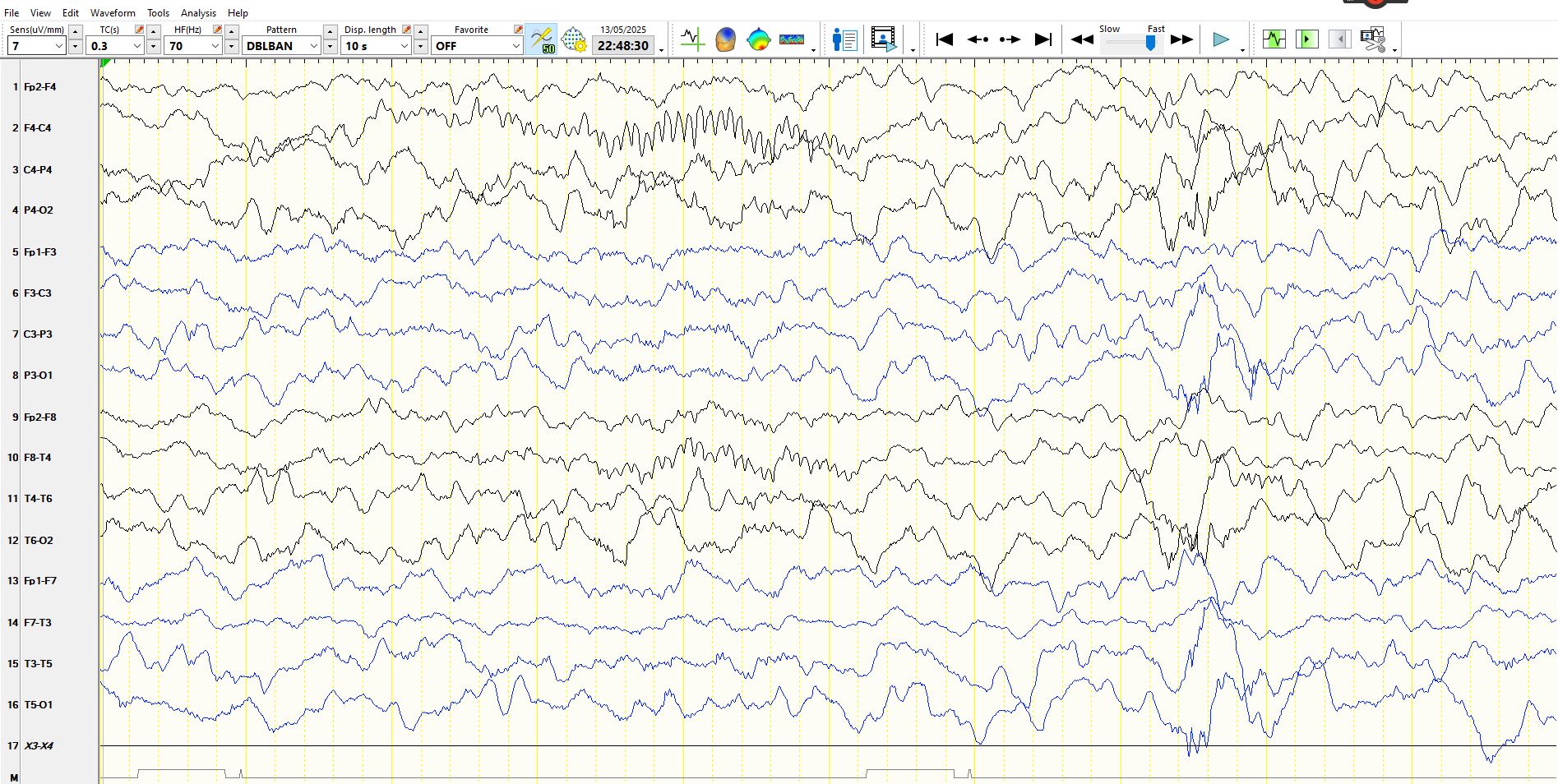
Above: right hemispheric spindles and polyspikes at 02-01-T5-T6 (bilateral occipital and posterior temporal regions). The usefulness of sleep for detection of inter-ictal epileptiform discharges is once again highlighted.